SEXTANT
 |
| Sextant |
One may also ask the meaning of sextant in Hindi ? Sextant
is called ( षष्ठक ) in Hindi Language. So, in
this article, I am going to discuss about the what exactly is a sextant?
(As written above!), How are its
inventors and its history in brief.
INVENTORS AND HISTORY OF THE SEXTANT
The first sextants were made of wood and brass, but later models were made of durable materials such as copper and iron. Most of them are very decorative and have a detailed carving on them. The use of sextants was common in the 19th century because it allowed sailors to navigate more accurately and safely. However, with the march of newer technologies and electronics in the 20th century, the use of sextants gradually declined. Today it is mostly used by sailors and sailors as a backup travel tool, as well as by hobbyists in celestial navigation.
 |
| John Hadley |
 |
| Thomas Godfrey |
PARTS OF A SEXTANT
A sextant is made up of different parts which are useful and have their own working sense. Here, is the list of parts from which a Sextant is made:
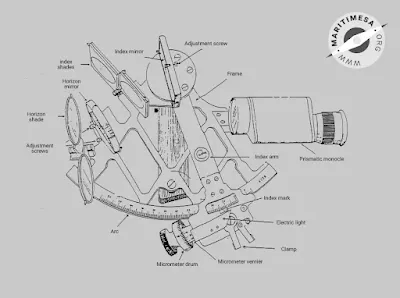 |
| Parts of a Sextant (credits to-maritimesa.org) |
- The frame.
- The handle.
- The telescope or monocle.
- The rising piece.
- The arc.
- The index arms.
- The clamp.
- The worm and rack.
- The micrometre drums.
- The micrometre vernier.
- Electric light.
- The index mirror.
- The index mirror clips.
- The index mirror (first) adjustment screw.
- The index mirror shades.
- The horizon mirror.
- The horizon mirror clips.
- The horizon mirror (second) adjustment screw.
- The horizon mirror (third) adjustment screw.
- The horizon mirror shades.
HOW TO USE A SEXANT ?
 |
| A man using Sextant |
- First, hold the sextant at eye level and look through the telescope to find the celestial object you wish to measure, such as the sun, moon, or stars.
- Use the index mirror and horizon mirror to align the image of the celestial object with the horizon line visible through the sextant.
- Adjust the micrometre drum until the two images are perfectly aligned, and then read the angle of elevation from the sextant's scale.
- Record the time of your measurement and use a reference table or chart to determine the object's position in the sky at that time.
- Use this information, along with your measured angle of elevation, to calculate your position on the Earth's surface using trigonometry.
- Repeat this process several times to ensure accuracy and take an average of your measurements to reduce errors.
- Finally, use your calculated position to update your navigation charts and adjust your course accordingly.
I
also know that the instructions are a bit complicated and that’s why I am
recommending everyone to see the References given below.
ADVANTAGES AND LIMITATIONS OF A SEXTANT
Advantages of a sextant:
- A sextant has many advantages, the advantages noted below are when sextant was in frequent uses during its period i.e., during 18th and 19th Century. Some of them are noted below as follows:
- Its lightweight and comes in handy when needed.
- It is very easy to use if the user knows the instructions for using it.
- Only needs and requires one person to use it.
- Using it, one can also guide the ship in right way and spot if he/her ship is lost from its way or not.
- Can also be used in daytime.
Limitations of a Sextant:
As
we all know that, as a thing has advantages, it has got some disadvantages,
too. Here are some of sextant’s limitation:
- It cannot be used in unbearable weather conditions like storms , etc.
- On a moonless night, horizon fades quickly and makes it difficult to use the sextant.
ERRORS IN A SEXTANT
There
can be some errors in the sextant. Here a short list and look of them. There as
two types of errors in a Sextant :
- Adjustable Errors (which can be adjusted on-board)
- Non-adjustable Errors (which cannot be adjusted on-board)
Adjustable Errors:
- The Perpendicularity Error
- Side Error
- Index Error
- The Error of Collimation
Non-adjustable Errors:
- Graduation Error
- Centring Error
- Shade Error
- Optical Error
- Wear on the rack and worm
A
detailed studied on them is done by Marine Insights. I recommend
you to visit their page for more detailed information.
HOW TO MAINTAIN AND TAKE CARE OF A SEXTANT ?
Here are some of the tips that all professional and experts recommend while taking care of a sextant:
- Keep the sextant in a dry and cool place when not in use to prevent corrosion and damage.
- Clean the lenses and mirrors regularly with a soft cloth to remove any dust or dirt.
- Check the alignment of the mirrors periodically to ensure accurate readings.
- Lubricate the moving parts of the sextant with a light oil to prevent rust and ensure smooth operation.
- Store the sextant in its case or cover when not in use to protect it from dust, moisture, and accidental damage.
- Avoid exposing the sextant to extreme temperatures or direct sunlight, as this can damage the delicate components.
- Have the sextant serviced by a professional if you notice any problems or if it has not been used for an extended period.
APPLICATIONS OF THE SEXTANTS
Here are some of the few applications of the
sextant:
- Navigation at Sea
- Aviation
- Astronomy
CONCLUSION
The
continuous progress the technology and modern devices has gave a toll on the
use of Sextant. Thus, resulting in the gradual decline in the use of Sextant. In
this article we have studied and had our views on its working, inventors and
its brief history, its application, its advantages and limitations and how to
take care of the Sextant and much more things.
In
conclusion, the sextant's historical significance, practical applications, and
timeless elegance make it a symbol of human ingenuity and the relentless
pursuit of exploration. While modern technology may have eclipsed its
prominence, the sextant's legacy lives on as a testament to the marvels of
human invention and its continued value in certain navigational scenarios. As
we cherish the advancements of the present, let us also remember the ingenuity
of the past and the instruments that shaped our understanding of the world. The
sextant stands as a beacon of human achievement, guiding us through the seas of
time and discovery.
REFERENCES AND CREDITS
Here is the list of websites, I recommend you to view
as they have tons of useful information that I haven’t included:
