Pantograph
 |
| Pantograph |
HISTORICAL BACKGROUND
 |
| Christopher Scheiner (credits to - wikipedia) |
The roots of the pantograph can be traced back
to the early 17th century when the first iterations of the device began to
emerge. It was Christopher Scheiner, a German Jesuit priest, who first
conceived the idea of a mechanical linkage that could duplicate drawings. Over
time, inventors and engineers like Georg Christoph Schott, William Wallace, and
William Hughes refined and improved the pantograph, establishing its
significance in various industries, making its applications in various fields
and now it has become a crucial part of our day-to-day in making huge art
structures and designs.
WORKING PRINCIPLE
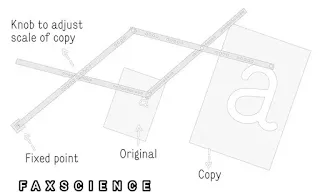 |
| Working of a Pantograph |
TYPES OF PANTOGRAPHS
Pantographs come in various
designs, each catering to specific applications. The most common types include
single-arm and double-arm pantographs.
- Single-arm pantographs
are often used for precision engraving, whereas double-arm pantographs
provide greater flexibility and stability for larger-scale copying tasks.
- In addition, digital
pantographs have emerged in recent years, combining mechanical elements
with digital technology to enhance the precision and streamline the design
process.
APPLICATIONS OF PANTOGRAPH
The versatility (the ability to
adapt) of pantographs has rendered them vital in numerous fields. In the realm
of art and drawing, pantographs have enabled artists to recreate and scale
their designs accurately. Architects and engineers have employed pantographs to
copy complex blueprints and plans, simplifying the replication process.
Pantographs have also found applications in the engraving industry, allowing
for the creation of intricate designs on various materials. Furthermore,
manufacturers have harnessed pantographs for scaling prototypes and patterns,
facilitating mass production.
ADVANTAGES AND LIMITATIONS
A Pantograph has several
advantages that have contributed to science and art. Its advantages are as
follow :
- Enabling precise
scaling of designs
- Ensuring accuracy
- Maintaining the
integrity of the original artwork
- Relatively easy to use
- Requires minimal
training and skill
- They are versatile
- Capable of reproducing designs
on different surfaces and materials
However, if
one thing has advantages to be gained, it also has disadvantages that have to
be accepted. Thus, the pantograph has its limitations too. Some of its
limitations are as follows:
1.
Need
for manual operation
2.
The
restricted size of the reproduced design
3.
Difficult
to use in larger projects as it tends to become large in size and difficult to
use
NOTEWORTHY USE CASE EXAMPLES
Throughout history, pantographs have played an important role in various significant endeavours. In the field of art, renowned artists like Albrecht Dürer and Leonardo da Vinci utilized pantographs to create scaled replicas of their masterpieces. Architects and engineers have employed pantographs to reproduce complex architectural drawings, preserving designs for future. Notably, pantographs have also been used in the currency printing industry to produce precise copies of banknotes, incorporating complicated security features.
 |
| A reference to Dr. Stone |
FUTURE DEVELOPMENT AND TRENDS
As technology continues to
advance, the field of pantograph is not immune to innovation, it will continue
to evolve too. Recent developments have seen the integration of digital
elements, combining mechanical pantographs with digital imaging and precision
control. These advancements have led to even higher levels of accuracy and
efficiency in design reproduction and additionally, the emergence of 3D
printing technology has opened new paths for pantographs, enabling the
replication of three-dimensional objects with complex details.
SUMMARY
In this
blog we have seen the working of the Pantograph, how invented it and its future.
We have also seen the advantages and limitations of the same and how it
impacted the world in the view of science and brought revolution in the fields
of technology , art and drawing .We also show that as technology
continues to advance, the future of pantographs holds even greater potential.
The integration of digital elements and 3D printing opens up exciting
possibilities for enhanced accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability in design
reproduction. So, whether it's a beautifully engraved piece of artwork, an
accurately reproduced blueprint, or a precisely scaled prototype, the
pantograph continues to serve as a reliable companion in the creative process.
As we embrace the digital age, let us not forget the mechanical marvels of the
past, for the pantograph stands as a symbol of our relentless pursuit of
perfection in design and our unwavering passion for creativity.
REFERENCES
Hope, you all enjoyed the article till the last !
! THANK YOU !
