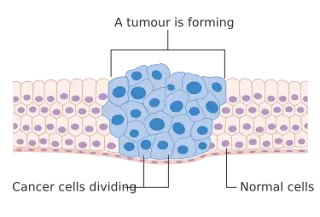
What is Cancer ?
Cancer is defined as a disease in which a cell becomes so uncontrollable and abnormal that it gains ability to infiltrate, multiply itself and destroy normal tissues. Want me to elaborate ? Then Cancer is a complex and complicated disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth and division of abnormal cells, which have the capacity to infiltrate surrounding tissues and spread to other parts of the body. This condition involves a large group of diseases united by a commonality: the transformation of normal cells into cancerous counterparts that grows uncontrollably, leading to the formation of tumors or the invasion of healthy tissues. The main characteristic of cancer is its propensity to disrupt the normal cellular regulation mechanisms, allowing for the uncontrolled growth and spreading of these abnormal cells. This barbaric cell is different from healthy cells because it grows too much and spreads where it shouldn't. This makes it hard to figure out, treat, and control.
What are some common types of Cancer ?
 |
| Credits : Flickr |
- Bladder Cancer
- Brain Cancer
- Breast Cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer (Colon and Rectum)
- Esophageal Cancer
- Kidney Cancer
- Leukemia
- Liver Cancer
- Lung Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Multiple Myeloma
- Ovarian Cancer
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Sarcoma
- Skin Cancer (including Melanoma)
- Stomach Cancer
- Testicular Cancer
- Thyroid Cancer
It's important to note that each type of cancer can have various subtypes with different characteristics and treatment approaches. Additionally, advancements in cancer and new addictions that we human will form will always lead to the discovery of new types or subtypes over time. If you have specific concerns or questions about cancer, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized information and guidance.
How is cancer developed ?
The development and birth of cancer cell is a complex process influenced by genetic mutations that disturb the normal functioning of cells. Under normal circumstances, genes regulate cell growth and division, ensuring that cells reproduce only when needed for the body's maintenance or repair. However, cancer cells undergo a transformation due to gene mutations, leading them to deviate from the usual course.
Gene mutations responsible for cancer development can be inherited, occur naturally over time as genes wear out, or result from exposure to factors like cigarette smoke, alcohol, or UV radiation from the sun. In short, these mutations turn a normal cell into a cancer cell, causing it to grow uncontrollably and resist the natural processes of maturity and cell death (yeah, the definition of cancer).
Cancer cells show uncommon characteristics that differ them from normal cells. They divide excessively, remain immature without fulfilling specific functions, evade the immune system (like we want to run away from our homes to play with our friends), ignore signals to cease division or undergo programmed cell death, and show a reduced ability to stick together, allowing them to spread to other parts of the body through the blood.
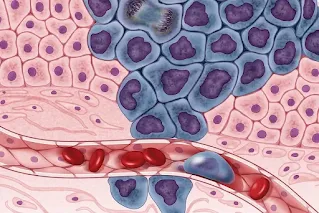
As cancer cells divide, they form a mass known as a tumor. To sustain their growth, tumors require a blood supply for oxygen and nutrients. Initially, small tumors can easily access nearby blood vessels. However, as tumors expand, they signal for the formation of new blood vessels, a process called angiogenesis. This mechanism not only supports tumor growth but also facilitates the spread of cancer cells to other parts of the body through the bloodstream.
The progression of cancer involves local invasion, where cancer cells infiltrate nearby tissues and structures, causing damage. Additionally, cancer can spread throughout the body, spreading from its original site to other regions of the body. This process is known as metastasis which occurs when cancer cells break away from the primary tumor, traveling through the blood to establish new colonies in distant locations.
Explaining the stages of Cancer and what they mean ?
Cancer staging is a systematic way of describing the
extent and spread of cancer in the body. It helps healthcare professionals
determine the prognosis and plan appropriate treatment. The stages are
typically denoted by Roman numerals (I-IV) or by descriptive terms such as
early, localized, regional, or distant. Here is a general overview of the
stages of cancer:
Stage 0 (In Situ):
- Cancer is in its earliest stage and has not invaded nearby tissues.
- Often referred to as "in situ," meaning the abnormal cells are present but have not spread.
Stage 1:
- Cancer is small and confined to its original location.
- It has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant sites.
Stage 2:
- Cancer is larger or has invaded nearby tissues, but it has not spread to lymph nodes or distant locations.
Stage 3:
- Cancer has invaded nearby tissues more extensively.
- It may have spread to nearby lymph nodes but not too distant sites.
Stage 4:
- Cancer has spread to distant organs or distant lymph nodes.
- This stage is often referred to as advanced or metastatic cancer.
The stages involve considering several factors:
Tumor Size (T): Describes the size of
the primary tumor.
- TX: Unable to evaluate the primary tumor.
- T0: No evidence of a primary tumor.
- T1, T2, T3, T4: Increasing size or extent of the primary tumor.
Lymph Node Involvement
(N): Indicates whether cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- NX: Lymph nodes cannot be evaluated.
- N0: No regional lymph node involvement.
- N1, N2, N3: Increasing extent of lymph node involvement.
Metastasis (M): Denotes whether
cancer has spread to distant organs.
- MX: Metastasis cannot be evaluated.
- M0: No distant metastasis.
- M1: Distant metastasis present.
For example, a breast cancer staging of T2N1M0 would indicate a relatively larger primary tumor (T2), involvement of nearby lymph nodes (N1), and no distant metastasis (M0).
How do I know if I have cancer ?
 |
| Credits to Flickr |
Well, we can know this by checking your symptoms with
the symptoms listed in here but they can vary from patient to patient. The
symptom list :
- Unintended Weight Loss
- Fatigue
- Pain
- Changes in Skin
- Changes in Bowel or Bladder Habits
- Persistent Cough or Hoarseness
- Difficulty Swallowing
- Lumps or Thickening
- Changes in Menstrual Cycle in case of women
- Difficulty Breathing
I will highly advice if you got any of the above symptoms,
immediately see a doctor.
Is there any treatment for cancer ?
Well, there are various treatment for cancer that’s
we, humans have developed. The choice of treatment that the patient will get will depend on the
type of cancer, its stage, and the overall health of the patient.
Yes,
there are various treatments available for cancer, and the choice of treatment
depends on the type of cancer, its stage, and the overall health of the
patient. Common cancer treatments include:
- Surgery: This involves the removal of the tumour or
affected tissue and is often used for solid tumours.
- Chemotherapy: The use of drugs to kill or slow the growth
of cancer cells. It can be taken orally or intravenously.
- Radiation Therapy: High doses of radiation are used to target
and destroy cancer cells or shrink tumours.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment boosts the body's immune
system to fight cancer. It includes therapies such as checkpoint inhibitors and
CAR-T cell therapy.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs are used to target specific molecules
involved in cancer cell growth. This type of therapy is often used for cancers
with specific genetic mutations.
- Hormone Therapy: This therapy is used for cancers that are
hormone-sensitive, such as breast and prostate cancers, to block or interfere
with hormone production.
- Stem Cell Transplant: This procedure involves replacing diseased or
damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells, often used in treating
blood-related cancers.
- Precision Medicine: Treatment is tailored to an individual's
specific genetic makeup, allowing for more personalized and targeted therapies.
- Cryotherapy: Cancer cells are frozen, often used for
certain skin and liver tumours. Like Senku did to Tsukasa (a reference to Dr.
Stone)
It's quiet notable that patients may receive a combination of these treatments, and the approach may evolve based on the response to therapy. Additionally, clinical trials may offer new and innovative treatments that are being tested for effectiveness. Such a treatment may be the AOH1996 which can be the future of cancer curing. The choice of treatment is determined by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including oncologists, surgeons, and other specialists, who consider various factors to provide the most effective and appropriate care for each patient.
How to prevent Cancer ?
Here are some tips that all doctors will give to you
and I will give the same to you. By incorporating these tips into your daily
life, you empower yourself to take proactive steps toward reducing your risk of
cancer and promoting your overall well-being. Though regular check-ins with
healthcare providers are always recommended. Anyways the tips are as follows :
Quitting Smoking and
Tobacco:
- Seek support from healthcare providers or smoking cessation programs to quit smoking or using tobacco.
- Engage in activities that help distract from the urge to smoke and surround yourself with a supportive environment.
Making Healthy Eating
Habits:
- Opt for balanced and varied diet rich in colorful fruits and vegetables, which are packed with cancer-fighting antioxidants.
- Consider consulting a healthcare provider or nutritionist for personalized dietary guidance to meet your specific needs.
Doing Regular Physical
Activity:
- Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine, aiming for at least 30 minutes most days of the week (Go to the freaking gym pal).
- Find activities you enjoy to make exercise a sustainable part of your lifestyle.
Getting Environmental
Awareness:
- Be aware of environmental toxins. Avoid exposure to substances such as asbestos, radon, and pesticides, which may contribute to an increased cancer risk and if had any contact, immediately wash with soap.
Having a Sun
Protection:
- Practice sun safety by using sunscreen with a high SPF, wearing protective clothing, and staying in the shade during peak sunlight hours to reduce the risk of skin cancer.
Maintaining a Healthy
Weight:
- Aim for a healthy weight by combining a balanced diet with regular exercise, aiming to achieve and sustain a body mass index (BMI) within a healthy range.
Having a Moderate
Alcohol Consumption:
- If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in limits, keeping within the recommended limits for your gender.
- I recommend no alcohol consumption at all.
Some Survival Stories of Cancer
I remember this particular case of Kusum who was a young mom at 29, with a 3-year-old son, when she found out she had Stage 4 lung cancer. People usually think only smokers get lung cancer, but Kusum never smoked, and no one in her family did either. Kusum's story had a lot of confusion in the beginning. She had headaches and face twitches, but doctors thought it was just migraines. When her husband Vivek got worried and went to a specialist, they found nodules in her brain. Doctors first thought it was Brain Tuberculoma, but later scans revealed it was Stage 4 lung cancer that had spread to her brain.
The doctors said she had only 6 months to live. In India, no one with her condition had lived for more than a year. Kusum and her husband were very sad at first, but then Kusum decided to fight back. She tried different treatments, but her health kept getting worse, and she even went into a coma. Kusum had a rare kind of cancer, and Vivek managed to get a new drug from the United States. It helped at first, but her body became resistant, and the cancer spread more.
Kusum spoke out about the lack of treatment options in India, and after a lot of effort, she became the first Indian to join a clinical trial. The treatment helped a bit, but she still had a paralysis attack in 2016. Later, her cancer care team told Vivek about a foreign drug that could help. After some struggle, she got the medicine for free, and it made a big difference. She went from being paralyzed to running a marathon.
Kusum spent time with her family, made memories, and helped raise awareness about cancer. She inspired many with her story. She fought against the 6-month life expectancy doctors gave her and lived for 7 years. Sadly, she passed away in February 2019. Even today, Kusum's husband Vivek and their son continue to raise awareness about cancer. They work to break the stigma around Stage 4 cancer and provide more treatment options. They remain advocates for cancer patients and keep inspiring others with Kusum's story of strength and bravery.
Future of Cancer Treatment
 |
| Credits to NIH |
References : Here, I am giving credits to the websites which I took and shared all this precious information from. I would recommend you all to visit their sites and surf them for deeper information and knowledge :
- What is cancer? (2021, October 11). National Cancer Institute.https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/what-is-cancer
- Professional, C. C. M. (n.d.-b). Cancer. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12194-cancer
- Cancer - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic. (2022, December 7). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20370588
- Bailar, J. C., & Gornik, H. L. (1997). Cancer undefeated. The New England Journal of Medicine, 336(22), 1569–1574. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199705293362206

.webp)